The temperature controller is a measurement device used on temperature control. Thermocouple-type and resistor-type temperature controllers measure temperature electronically, obtaining the temperature change from the sensor and sending the measured data to the electronic processor. The output device will then control the temperature variation within a specific range.
Commonly, the use of temperature sensors is to measure temperature in circuits, which control a variety of equipment.
There various kinds of temperature sensors used to include resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, thermistors, infrared sensors, and semiconductor sensors. Every sensor uses particular operating parameters. These sensors have multiple varieties, but a standard procedure to measure temperature by sensing a change in the physical characteristic.
The temperature controller takes an input from a temperature sensor and has an output that is connected to a control element such as a heater or fan. It takes a measurement and compares it with desired value, and in case there is an error (deviation), it decided how much cooling or heating is required to bring the temperature back to normal.
To accurately control process temperature without extensive operator involvement, a temperature control system relies upon a controller, which accepts a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD as input.
An on-off temperature controller, also called a signaller or “bang-bang” controller, has a set a value, and as the process value increases, it brings it below to the desired temperature setpoint. As the process temperature rises above the setpoint, the output is changed to make it fall.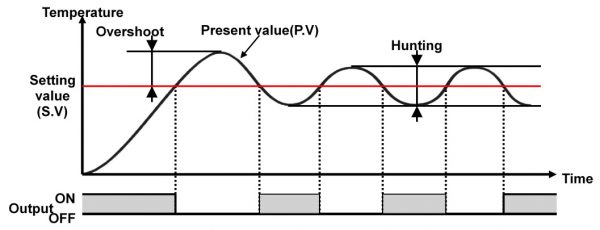
PID temperature control is a loop control to improve the accuracy of the process. PID temperature controllers work using a formula to calculate the difference between the desired temperature set point and current temperature, then predicts how much power to use in subsequent process cycles to ensure the process temperature remains as close to the set point.
If the PID temperature controller is tuned properly it will compensate the disturbance and bring the process temperature back to the set point, and reduce power as temperature approaches the set point so that it doesn’t overshoot and risk damaging the product with too much heat.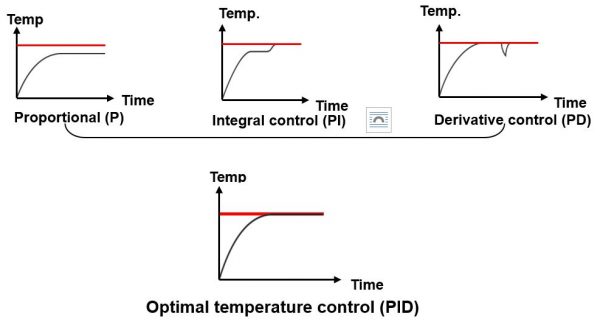
ON/OFF control action often involves the waveform shown in the following diagram. A temperature rise that exceeds the set point after temperature control starts is called overshooting. Temperature oscillation near the set point is called hunting. Improved temperature control is to be expected if the degree of overshooting and hunting are low.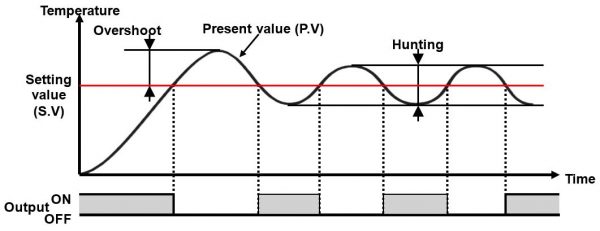
- DTI Series

- DTM Series

- DTK Series

- DT3 Series

- DTB Series

- DTC Series

- DTV Series

- DTE Series


